
After the release of the FY2022 budget requests to Congress, the military departments also posted their Unfunded priorities/requirements lists for the Congressional Armed Services Committees. Overseas Contingency Operations (OCO) is now replaced by 'direct war and enduring costs', which are now migrated into the budget. īy military department, the Army's portion of the budget request, $173 billion, dropped $3.6 billion from the enacted FY2021 budget the Department of the Navy's portion of the budget request, $211.7 billion, rose 1.8% from the enacted FY2021 budget, largely due to the 6% increase for the Marine Corps' restructuring to a littoral combat force (Navy request: $163.9 billion, or just 0.6% over FY2021, Marine Corps request: $47.9 billion, a 6.2% increase over FY2021) the Air Force's $156.3 billion request for FY2022 is a 2.3% increase over FY21 enacted budget the Space Force budget of $17.4 billion is a 13.1% increase over FY21 enacted budget. The National Defense Authorization Act, budgeting $740 billion for defense, was signed 27 December 2021. On 22 July 2021 the Senate Armed Services Committee approved a budget $25 billion greater than the President's defense budget request for FY2022. The total FY2022 defense budget request, including the Department of Energy, was $753 billion, up $12 billion from FY2021's budget request. In May 2021, the President's defense budget request for fiscal year 2022 (FY2022) was $715 billion, up $10 billion, from FY2021's $705 billion. The United States' military spending in 2021 reached $801bn a year according to the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute.
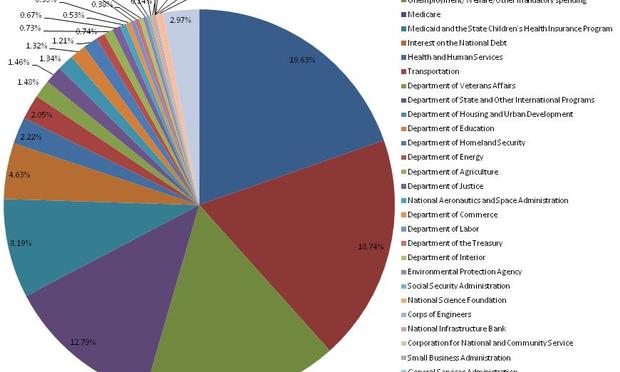
The President signed the FY2023 Appropriations bill on 23 December 2022. By 16 December 2022 the current budget extension resolution will have expired. As of 12 December 2022 the House and Senate versions of the Fiscal Year 2023 National Defense Authorization bill (FY2023 NDAA) were to be $839 billion, and $847 billion, for the HASC, and SASC respectively, for a compromise $857.9 billion top line. Īs of 4 April 2022 the FY2023 presidential budget request of $773 billion included $177.5 billion for the Army, $194 billion for the Air Force and Space Force, and $230.8 billion for the Navy and Marine Corps (up 4.1% from FY2022 request). By 9 March 2022Ī bipartisan agreement on a $782 billion defense budget had been reached (as part of an overall $1.5 trillion budget for FY2022 -thus avoiding a government shutdown). Budget for FY2023 Īs of 2 March 2022, the defense department was still operating under a continuing resolution, which constrains spending even though DoD has to respond to world events, such as the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine the FY2023 defense budget request will exceed $773 billion, according to the chairman of the House Armed Services Committee. The $886 billion National Defense Authorization Act is facing reconciliation of the House and Senate bills after passing both houses 27 July 2023 the conferees have to be chosen, next. The debt ceiling was suspended until 2025. In January 2023 Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen announced the US government would hit its $31.4 trillion debt ceiling on 19 January 2023 the 'X date' on which the US government would no longer be able to use 'extraordinary measures' such as issuance of Treasury securities is estimated to be in June 2023. military: the Army, Navy, Marine Corps, Air Force, Coast Guard, and Space Force.Īs of 10 March 2023 the FY2024 presidential budget request was $842 billion. The budget funds six branches of the U.S. The military budget pays the salaries, training, and health care of uniformed and civilian personnel, maintains arms, equipment and facilities, funds operations, and develops and buys new items. The military budget is the largest portion of the discretionary United States federal budget allocated to the Department of Defense, or more broadly, the portion of the budget that goes to any military-related expenditures. in constant 2019 US$ billions Military spending as a percent of Federal Government revenue Military budget of China, USSR, Russia and U.S.

Yearly spending of the United States military
#FEDERAL SPENDING PIE CHART DOWNLOAD#
" Historical Tables," Download "Table 8.5-Outlays for Mandatory and Related Programs: 1962–2025." " 2016 Annual Report of the Boards of Trustees of the Federal Hospital Insurance and Federal Supplementary Medical Insurance Trust Funds,". " Tax Freedom Day 2015 Is April 24th."Ĭenters for Medicare and Medicaid Services. " Historical Budget Data," Download "Jan. " H.R.83-Consolidated and Further Continuing Appropriations Act, 2015."Ĭongressional Budget Office. " Historical Tables," Download "Table 1.1-Summary of Receipts, Outlays, and Surpluses or Deficits (-): 1789–2025."


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
